CWDM Vs DWDM
CWDM
A CWDM system commonly supports eight wavelengths per fiber and is designed for short-range communications, using wide-range frequencies with wavelengths spread far apart.
Since CWDM is based on 20-nm channel spacing from 1470 to 1610 nm, it’s typically deployed on fiber spans up to 80km or less because optical amplifiers cannot be used with large spacing channels. This wide spacing of channels allows the use of moderately priced optics. However, the capacity of the links as well as the distance supported are less with CWDM than with DWDM.
Generally, CWDM is used for lower cost, lower capacity (sub-10G) and shorter distance applications where cost is an important factor.
More
recently, the prices for both CWDM and DWDM components have become
reasonably comparable. CWDM wavelengths are currently capable of
transporting up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet and 16G Fiber Channel, and it is
quite unlikely for this capacity to further increase in the future.
DWDM
In DWDM systems, the number of multiplexed channels is much denser than CWDM because DWDM uses tighter wavelength spacing to fit more channels onto a single fiber.
Instead of the 20 nm channel spacing used in CWDM (equivalent to approximately 15 million GHz), DWDM systems utilize a variety of specified channels spacing from 12.5 GHz to 200 GHz in the C-Band and sometimes the L-band.
Today’s DWDM systems typically support 96 channels spaced at 0.8 nm apart within the 1550 nm C-Band spectrum. Because of this, DWDM systems can transmit a huge quantity of data through a single fiber link as they allow for many more wavelengths to be packed onto the same fiber.
DWDM is optimal for long-reach communications up to 120 km and beyond due to its ability to leverage optical amplifiers, which can cost-effectively amplify the entire 1550 nm or C-band spectrum commonly used in DWDM applications. This overcomes long spans of attenuation or distance and when boosted by Erbium Doped-Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs), DWDM systems have the capability to carry high amounts of data across long distances spanning up to hundreds or thousands of kilometers.
In addition to the capability of
supporting a greater number of wavelengths than CWDM, DWDM platforms are
also capable of handling higher speed protocols as most optical
transport equipment vendors today commonly support 100G or 200G per
wavelength while emerging technologies are allowing for 400G and
beyond.
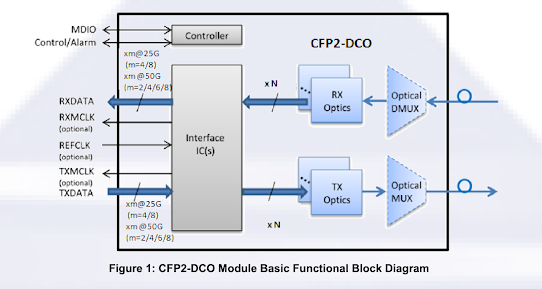
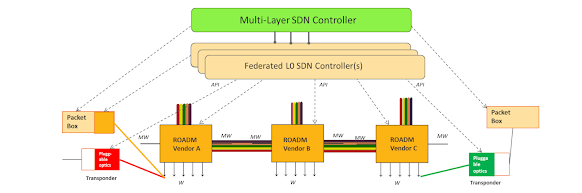
Comments
Post a Comment