What is SerDes (Serializer/Deserializer)?
SerDes is a functional block that Serializes and Deserializes digital data used in high-speed chip-to-chip communication. Modern SoCs for high-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI), automotive, mobile, and Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications implement SerDes that can support multiple data rates and standards like PCI Express (PCIe), MIPI, Ethernet, USB, USR/XSR.
A SerDes implementation includes parallel-to-serial (serial-to-parallel)
data conversion, impedance matching circuitry, and clock data recovery
functionality. The primary role of SerDes is to minimize the number of
I/O interconnects.
SerDes applications
SerDes is the most fundamental building block of a physical layer for chip-to-chip interconnect systems:
SerDes + Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) = PHY or Physical Layer
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model defines physical layer, or PHY, as an abstraction layer responsible for transmission and reception of the data. It is the lowest layer in the OSI model, which also includes:
- Application layer
- Presentation layer
- Session layer
- Transport layer
- Network layer
- Datalink layer
Different protocols suggest various abstraction division for a PHY. For example, 100G PHY defined by IEEE 802.3 has the following abstraction layers:
In this model SerDes will implement PMA/PMD sublayers, which is the
logical sub-block responsible for interface initialization, encoding
decoding, and clock alignment.
Reference links:
https://www.synopsys.com/glossary/what-is-serdes.html
https://www.electronicdesign.com/technologies/analog/article/21132088/why-do-we-need-serdes
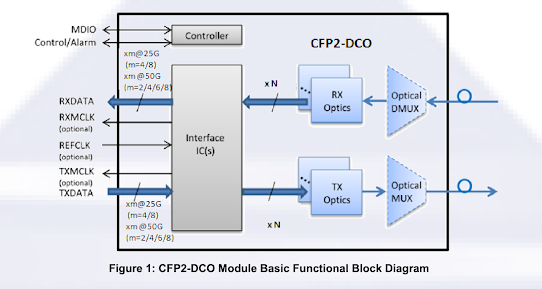
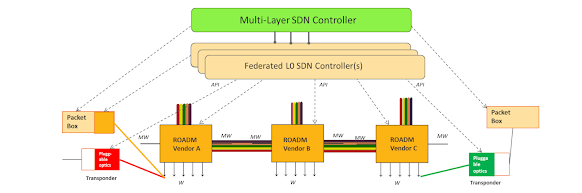
Comments
Post a Comment