DGE or Dynamic Gain Equalizer
A Dynamic Gain Equalizer (DGE) is a device used in optical communication systems to manage the gain variations of optical signals in different wavelength channels. It plays a crucial role in maintaining a balanced and consistent signal quality across multiple wavelengths, especially in wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) systems where multiple channels of data are transmitted simultaneously. Here's how a dynamic gain equalizer works:
Understanding Gain Variation: In optical communication systems, signal gain can vary across different wavelengths due to factors like fiber dispersion, amplifier characteristics, and other optical components. This gain variation can lead to unequal signal strengths in different wavelength channels, potentially causing performance issues.
Principle of Operation: A dynamic gain equalizer works by adjusting the gain of individual wavelength channels to achieve uniform signal levels across all channels. It dynamically modifies the gain of the optical signals to equalize their strengths.
Optical Filter Array: A DGE often employs an array of optical filters that selectively attenuate or amplify specific wavelength channels. These filters are typically based on technologies such as thin-film filters, fiber Bragg gratings, or liquid crystal devices.
Feedback Control: The DGE uses feedback control mechanisms to continuously monitor the signal strengths of different wavelength channels. Optical power monitors are used to measure the signal power of each channel, and this information is fed back to the DGE's control circuitry.
Gain Adjustment: Based on the feedback from the optical power monitors, the DGE's control circuitry calculates the required gain adjustments for each channel. It then adjusts the attenuation or amplification levels of the optical filters in real-time to achieve the desired equalization.
Adaptive Equalization: DGEs are adaptive devices, meaning they continuously monitor and adjust the gain as the optical signals and network conditions change. This adaptability is important to handle variations caused by factors like network changes, equipment aging, and environmental conditions.
Non-Destructive Process: The equalization process performed by a DGE is non-destructive, meaning it doesn't alter the content of the optical signals. It only modifies the signal strength to achieve uniform power levels across different channels.
Network Management Integration: DGEs can be managed and controlled remotely as part of the overall network management system. Network operators can configure and monitor the performance of DGEs to ensure optimal signal quality and transmission.
Applications: DGEs are commonly used in WDM optical communication systems, such as long-haul and metro networks, where maintaining consistent signal levels across multiple wavelength channels is essential for reliable data transmission.
In summary, a Dynamic Gain Equalizer (DGE) is an optical device that dynamically adjusts the gain of individual wavelength channels in optical communication systems. By equalizing the signal strengths, DGEs help to ensure consistent and balanced signal quality, contributing to the reliable and efficient operation of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) networks.
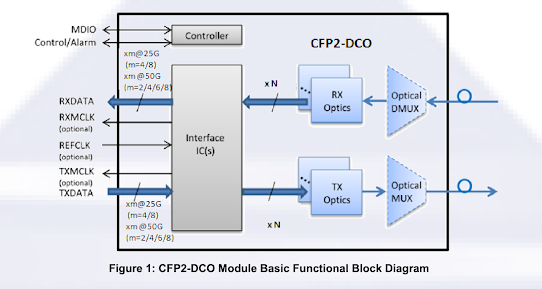
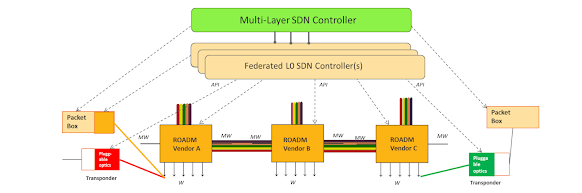
Comments
Post a Comment